RX Pad Blog
Clinical Decision Support System Alerts

HD. After week (W) 96, participants transitioned to daily B/F/TAF to assess whether efficacy and safety would be maintained on this STR that is guidelines-recommended for PLWH with eGFR > 30 mL/min.
Methods. Virologically suppressed adult PLWH with ESRD on chronic HD who completed W96 on E/C/F/TAF enrolled in the B/F/TAF extension for 48 weeks. Efficacy was assessed as the proportion of participants with virologic suppression (HIV RNA < 50 copies/mL). Safety was assessed throughout the study, PK was assessed using sparse sampling at W4, 24 and 48.
Results. 55 enrolled, 36 completed E/C/F/TAF, 10 entered the B/F/TAF extension. The median age was 55 yrs (range 34-63); median time on HD was 4 yrs (range 2-16). All ten participants on B/F/TAF had HIV-1 RNA < 50 c/mL (95% CI 69%, 100%) at W48. All participants had at least 1 adverse event (AE); most were grade 1 or 2 in severity. One participant had a grade 3 AE and 3 had serious AEs; none were considered related to study drug by the investigator. One participant had AEs attributed to study drug (malaise grade 1 and nausea grade 2), which resolved and did not lead to discontinuation of study drug. There were no clinically relevant changes in fasting lipids. In participants with evaluable data (n=2-5 per timepoint), mean bictegravir trough concentrations were lower compared to PLWH not on HD but remained 4- to 7-fold higher than the established protein-adjusted 95% effective concentration (paEC95) of 162 ng/mL against wild-type virus.
Conclusion. A once daily regimen of B/F/TAF maintained virologic suppression in PLWH on chronic HD. B/F/TAF was well-tolerated with no discontinuations. B/F/ TAF may be an effective, safe and convenient once daily STR and ameliorate the need for dose adjustment in appropriate PLWH who require chronic HD.
Disclosures. Joseph J. Eron, MD, Gilead Sciences (Consultant, Research Grant or Support)Janssen (Consultant, Research Grant or Support)Merck (Consultant)ViiV Healthcare (Consultant, Research Grant or Support) Aimee Wilkin, MD, MPH, Gilead Sciences Inc. (Grant/Research Support, Scientific Research Study Investigator, Advisor or Review Panel member)GlaxoSmithKline (Grant/Research Support)Janssen (Grant/Research Support, Scientific Research Study Investigator, Advisor or Review Panel member)Pfizer (Grant/Research Support) Moti Ramgopal, MD FACP FIDSA, AbbVie (Speaker’s Bureau)Allergan (Speaker’s Bureau)Gilead Sciences Inc. (Consultant, Scientific Research Study Investigator, Speaker’s Bureau)Janssen (Speaker’s Bureau)Merck (Consultant)Viiv Healthcare (Consultant) Olayemi Osiyemi, M.D, GlaxoSmithKline (Advisor or Review Panel member, Speaker’s Bureau)ViiV Healthcare (Advisor or Review Panel member, Speaker’s Bureau) Jihad Slim, MD, Abbvie (Speaker’s Bureau)Gilead (Speaker’s Bureau)Jansen (Speaker’s Bureau)Merck (Speaker’s Bureau)ViiV (Speaker’s Bureau) David Asmuth, MD, Gilead Sciences Inc. (Scientific Research Study Investigator) Edwin DeJesus, MD, Gilead Sciences (Advisor or Review Panel member) Polina German, PharmD, Gilead Sciences (Employee) Christiana Blair, MS, Gilead Sciences (Employee, Shareholder) Christoph C. Carter, MD, Gilead Sciences Inc. (Employee, Shareholder) Diana M. Brainard, MD, Gilead Sciences (Employee) Sean E. Collins, MD, MS, Gilead Sciences (Employee) Hal Martin, MD, MPH, Gilead Sciences Inc. (Employee, Shareholder) 1003.
BIC/FTC/TAF Maintains Viral Suppression in Patients with Documented M184V/I Mutations: A Real World Experience Nicholas Chamberlain, MD1 ; James B. Brock, MD, MSCI, FACP1 ; Leandro A. Mena, MD, MPH1 ; 1 University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, Mississippi
Session: P-47. HIV:
Treatment Background. The M184V/I mutation is a common mutation in treatment-experienced patients with HIV and confers high-level resistance to lamivudine and emtricitabine. Our objective is to assess the effectiveness of bictegravir (BIC)/emtricitabine (FTC)/tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) in a real-world setting in achieving and maintaining viral suppression in patients with documented M184V/I mutations.
Methods. This case series is comprised of treatment-experienced HIV-positive patients with documented historical or newly-identified M184V/I mutations who were placed on BIC/FTC/TAF as a switch strategy or as therapy for patients who had failed a prior regimen. Patients with any resistance to tenofovir or bictegravir were excluded. Our primary outcome was sustained viral suppression at 12 months after initiation of BIC/FTC/TAF.
Results. We included 33 patients (94% black, 52% male, median age 49, range 36-63) with an M184V/I mutation. The majority (91%) showed sustained viral suppression at 12 months of treatment. Non-adherence to medication was the common factor in all three cases of treatment failure. One patient developed an R263K mutation while on therapy, which conferred low-level resistance to bictegravir. There were no other instances of newly-acquired resistance to any of the components of BIC/FTC/TAF.
Conclusion. Our results demonstrate high success rates of BIC/FTC/ATF in achieving and maintaining viral suppression in patients with documented M184V/I mutations who adhere to medications in a real-world setting with a single instance of new treatment-emergent resistance to bictegravir. These findings are congruent with reported sub-group analysis in clinical trial data and support the use of BIC/FTC/TAF in patients with M184V/I mutations.
Disclosures. Leandro A. Mena, MD, MPH, Binx Health (Grant/Research Support)Evofem (Grant/Research Support)Gilead Science (Consultant, Grant/ Research Support, Speaker’s Bureau)GSK (Grant/Research Support)Janssen (Grant/ Research Support)Merck (Consultant, Grant/Research Support)Roche Molecular (Consultant, Grant/Research Support)SpeedDx (Grant/Research Support)ViiV Healthcare (Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker’s Bureau)
1004. Clinical Decision Support System Alerts for HIV Retention in Care – A Pilot Implementation Research Study Michael Leonard, MD1 ; Rachel P. Weber, PhD2 ; Laurence Brunet, PhD2 ; Bernard Davis, PhDc, MBA3 ; Christopher Polk, MD1 ; Joel Wesley Thompson, MHS, PA-C, AAHIVS, DFAAPA, MHS, PA-C, AAHIVS, DFAAPA4 ; Jennifer S. Fusco, BS2 ; Tammeka Evans, MoP5 ; Pedro Eitz Ferrer, PhD, Master of Health Communication6 ; Rodney Mood, BS, MBA2 ; Gregory Fusco, MD, MPH2 ; 1 Atrium Health, Charlotte, North Carolina; 2 Epividian, Inc., Durham, North Carolina; 3 RAO Community Health, Charlotte, North Carolina; 4 Amity Medical Group, Charlotte, North Carolina; 5 ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC; 6 TBWA/WORLDHEALTH, New York, New York
Session: P-47.
HIV: Treatment Background. Clinical decision support system (CDSS) alerts may help retain people living with HIV (PLWH) in care. A system of CDSS alerts utilizing the CHORUS™ portal was developed to identify PLWH at risk of being lost to care. To evaluate feasibility for a larger scale study, a before and after implementation research pilot study was implemented in the OPERA Cohort at three clinic sites in a southeastern US city.
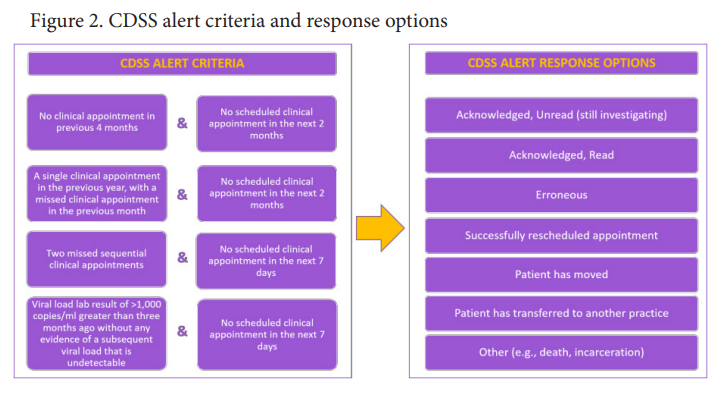
Methods. Periods without intervention (before) or with CDSS alerts (after) were followed by 3 months of follow up. The study population consisted of PLWH with ≥ 1 electronic health record entry in the 2 years prior to, or during, the before or after period (Fig 1). To support clinicians through a discrete implementation strategy, alerts warning of suboptimal patient attendance were generated daily for the eligible PLWH at each site; providers or other clinic staff could respond to the alerts (Fig 2). Alerts, responses, and visits (i.e., meeting with provider or HIV lab measurement) were characterized. The proportion of PLWH with ≥ 1 visit in the before and after periods were compared at each site by Pearson’s Chi-square.
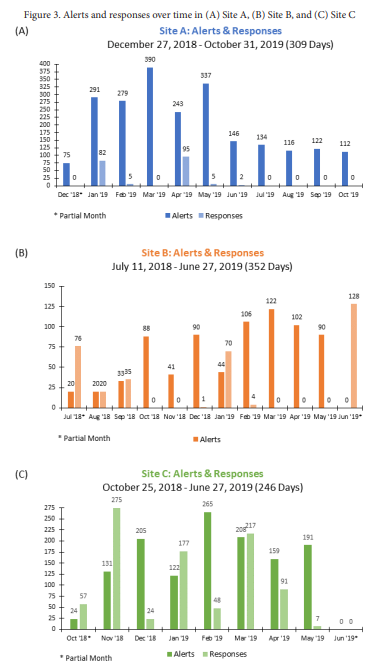
Results. A total of 12,230 PLWH were eligible (sites A: 11,271; B: 733; C: 1,344 PLWH), with > 75% in both the before and after periods. The ratio of alerts to responses was 11.9 at site A (2,245 alerts to 189 responses in 309 days; Fig 3A), and comparatively lower at sites B (756 alerts to 334 responses in 352 days, ratio=2.2; Fig 3B) and C (1,305 alerts to 896 responses in 246 days, ratio=1.5; Fig 3C). Responses to alerts were sporadic at sites A and B and consistent at site C. After the intervention, the proportion of PLWH with ≥ 1 visit stayed the same at site A (46% in both periods; p=0.47), decreased at site B (91% to 80%; p< 0.01), and increased at site C (72% to 81%; p< 0.01).
Conclusion. This pilot study was ecological by design: measures of retention in care were compared over two calendar periods, without accounting for changes in study populations, clinic characteristics, and policies in place over time (which could have impacted clinic attendance). Though engagement with the CDSS was suboptimal at some sites, this implementation pilot study has demonstrated the ability to implement a CDSS aimed at identifying at-risk PLWH, while highlighting areas for improvement in future larger scale studies.
Disclosures. Joel Wesley Thompson, MHS, PA-C, AAHIVS, DFAAPA, MHS, PA-C, AAHIVS, DFAAPA, Gilead (Shareholder, Speaker’s Bureau)Janssen (Speaker’s Bureau)Theratechnologies (Speaker’s Bureau)ViiV (Speaker’s Bureau) Tammeka Evans, MoP, ViiV Healthcare (Employee)
1005. Comparison of Weight Changes in Treatment-Naïve, HIV-Infected Patients Receiving Integrase Inhibitor-Based Therapy Versus Protease Inhibitor-Based Therapy Zachary Howe, PharmD1 ; Eric Farmer, PharmD, BCPS, AAHIVP2 ; Brooke Stevens, PharmD, BCPS, AAHIVP2 ; Emily Huesgen, PharmD, BCACP, AAHIVP3 ; 1 Indiana University Health AHC, Indianapolis, Indiana; 2 Indiana University Health LifeCare Clinic, Indianapolis, Indiana; 3 Indiana University Health, Ellettsville, Indiana
Session: P-47. HIV:
Treatment Background. Recent data regarding integrase inhibitor (INSTI) therapy indicate possible association with weight gain. The incidence and degree of weight gain seems to vary by both patient-specific and regimen-related factors, such as nucleoside reverse transcriptase (NRTI) backbone.
Methods. This was a retrospective chart review of previously ART-naïve Indiana University Health LifeCare Clinic patients who started an INSTI- or PI-based regimens from 1/1/13 to 7/31/19. Adult patients without prior ART exposure receiving an INSTI- or PI-based regimen for at least 10 months were included. The primary objective was weight gain at 12 months after starting ART. Subgroup analyses were conducted by INSTI, PI, or NRTI backbone utilized. Statistical testing included Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test and Chi Square analyses.
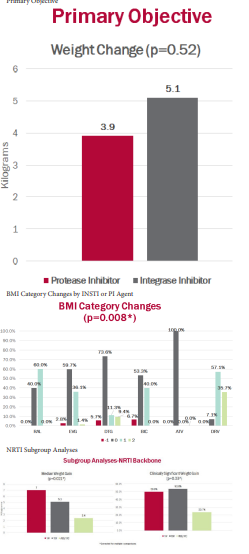
Results. The patient population (N=162) was predominately male and African American with relative immunocompetence, generally achieving viral suppression after 12 months of ART. Patients receiving PI-based therapy were more likely to be Asian American or Hispanic (p=0.04), and to receive a tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)-based regimen (p=0.0034). No statistically significant difference in weight change was observed between INSTI- and PI-based regimens (median weight gain 5.1 kg vs 3.9 kg, p=0.52). The proportion of obese or overweight patients in the INSTI arm increased significantly as compared to baseline (p=0.00001). Subgroup analyses demonstrated significant increases in weight gain and clinically significant weight gain with tenofovir-based (tenofovir alafenamide and TDF) regimens compared to those with abacavir/lamivudine (p< 0.05).

Authors: Michael Leonard, Rachel P Weber, Laurence Brunet, Bernard Davis, Christopher Polk, Joel Wesley Thompson, Jennifer S Fusco, Tammeka Evans, Pedro Eitz Ferrer, Rodney Mood, Gregory Fusco.